프로그래밍/자바
[자바의 정석] Ch 11 총정리 - 2
dandev
2022. 7. 30. 22:05
반응형
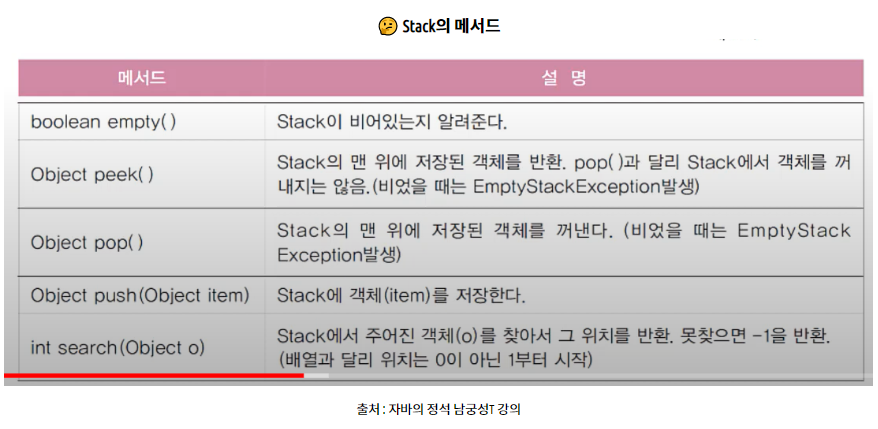
🤔 Stack
✔ LIFO(Last In First Out)
마지막에 저장된 것을 먼저 꺼냄.
저장(push), 추출(pop)
🤔 Queue
✔ FIFO(First In First Out)
제일 먼저 저장한 것을 먼저 꺼냄.
따라서 LinkedList가 적합함!!
저장(offer), 추출(poll)


다음의 예제를 통해 스택과 큐에 대해 이해하자.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex11_4 {
static Queue q = new LinkedList();
static final int MAX_SIZE = 5; // Queue에 최대 5개까지만 저장
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("help를 입력하면 도움말을 볼 수 있습니다.");
while (true) {
System.out.println(">>");
try {
// 화면으로부터 라인단위로 입력받음.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = sc.nextLine().trim();
if ("".equals(input)) continue;
if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("q")) {
System.exit(0);
} else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("help")) {
System.out.println("help - 도움말을 보여줍니다.");
System.out.println("q 또는 Q - 프로그램을 종료합니다.");
System.out.println("history - 최근에 입력한 명령어를 "
+ MAX_SIZE + "개 보여줍니다.");
} else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("history")) {
save(input); // 입력받은 명령어를 저장하고,
// LinkedList의 내용을 보여줌.
LinkedList list = (LinkedList) q;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + "." + list.get(i));
}
} else {
save(input);
System.out.println(input);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("입력 오류입니다.");
}
} // while(true)
} // main()
public static void save(String input) {
// queue에 저장한다.
if (!"".equals(input)) // if(input!=null&&!input.equals("")랑 같은말
q.offer(input);
// queue의 최대크기를 넘으면 맨 처음 입력된 것 삭제
if (q.size() > MAX_SIZE) { // size()는 Collection인터페이스에 정의
q.remove();
}
}
}// end of class
반응형